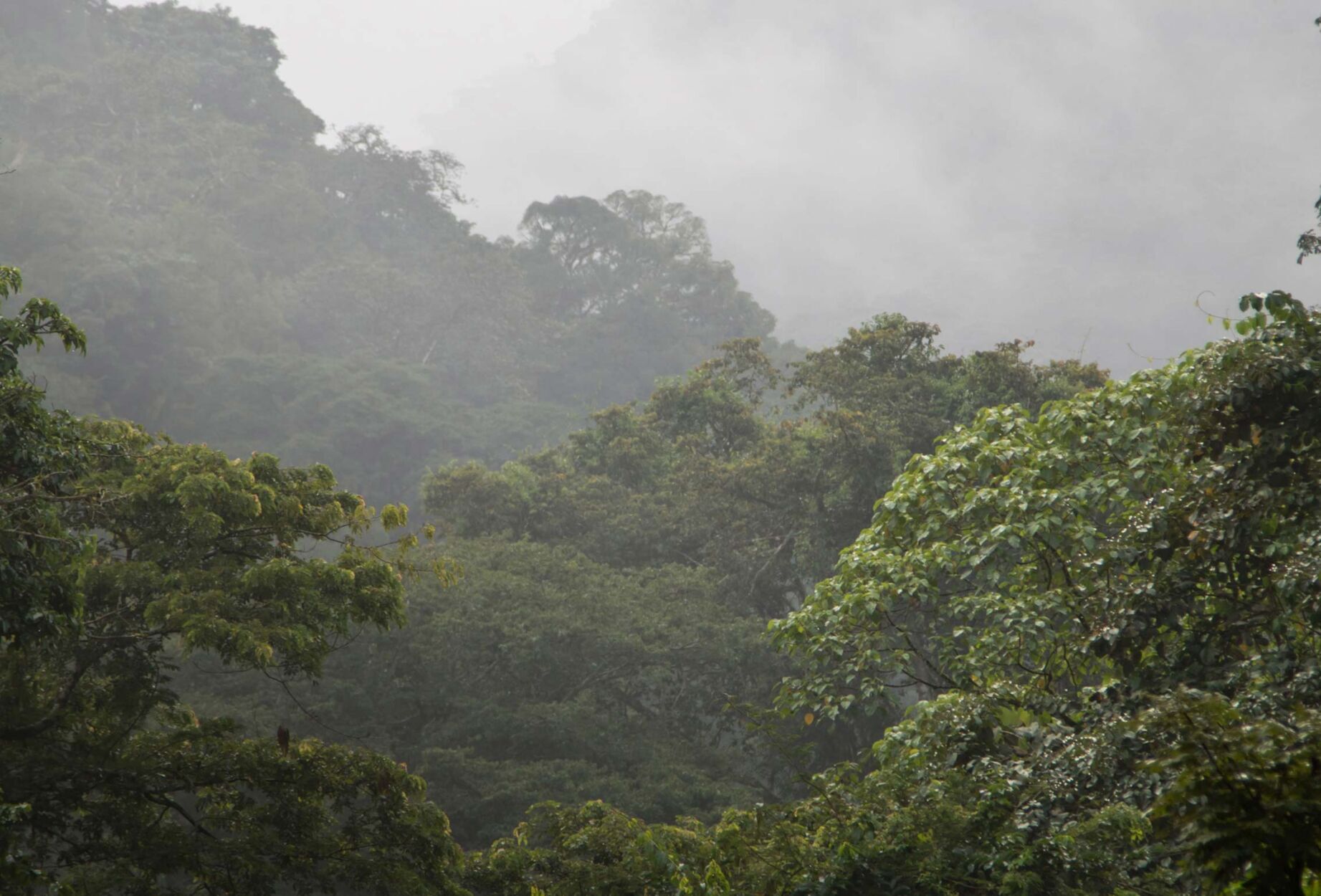
The Yayu Forest Coffee Biosphere Reserve is home to one of the few remaining areas of intact Afromontane rain forests in Ethiopia, with wild Arabica coffee providing home and income to numerous communities. The multiple economic and natural values of the area are recognised by its designation as a national gene reserve for wild Arabica coffee, a UNESCO biosphere reserve and IBA sites of international significance. Importantly, the local name is actually "Yayo," but it was registered as "Yayu" under UNESCO.
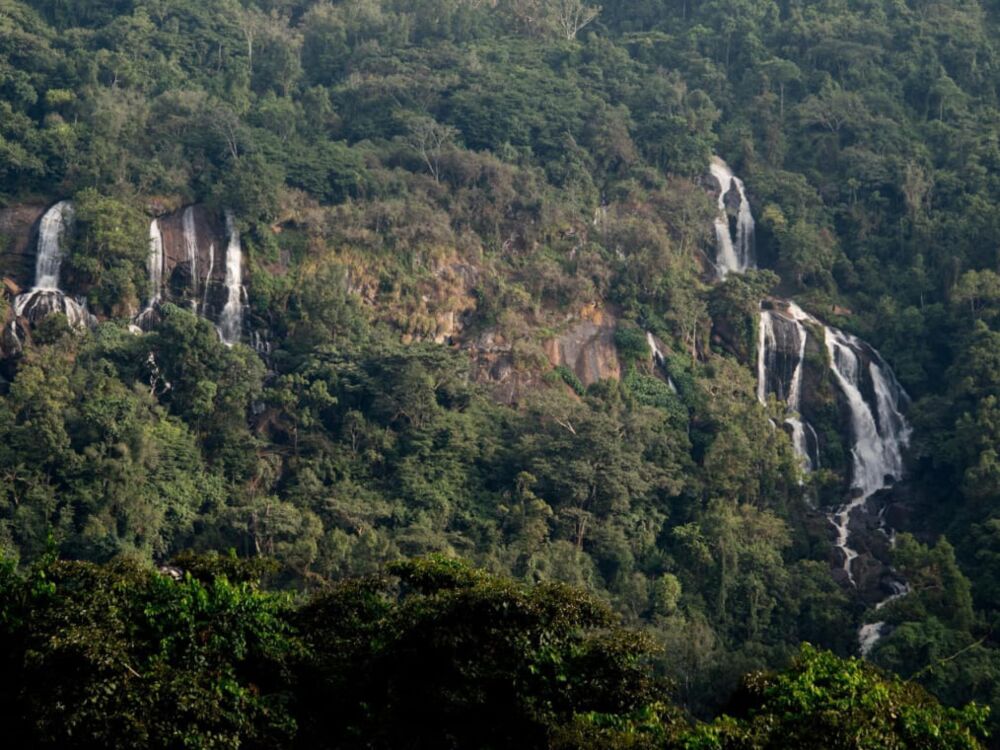

Where Montane Rainforests and Coffee Culture Converge
With lush montane rainforests, wetlands, grazing land and smallholder farming areas, caves and waterfalls, the landscape offers incredible scenery. Contributing to the name of the Biosphere Reserve, coffee has an unprecedented economic importance for Ethiopia, but also plays a central role in Ethiopian culture. In the area, coffee is cultivated in various ways: as garden-coffee in family home gardens, as well as in some plantations, but predominantly as forest coffee under the canopy of old growth trees.

Preserving Ethiopia's Natural and Cultural Treasures
In the core zone, the primary forest vegetation is conserved, which also plays an important role for watershed protection. Small and big rivers like Geba, Dogi, Saki and Sese, discharge into the Baro River, a main tributary of the river Nile. Internationally, The Biosphere Reserve holds an important role in protecting one of the few last remnants of Afromontane cloud forests. Forming part of the Eastern Afromontane Biodiversity hotspot, the Yayu Coffee Forest Biosphere Reserve is not just an important gene reserve for the wild populations of Coffea arabica, but also home to numerous other plant and animal species which are considered under threat of extinction or are found nowhere else than in these kinds of cloud forests. The all-encompassing cultural and historical significance of the area is manifested in many archaeological and ritual sites.

The Yayu Coffee Forest Biosphere Reserve is a unique place of immense importance, where environmental value blends with cultural heritage. It faces challenges, but also holds the potential for the sustainable coexistence of nature and human livelihoods, guided by a rich cultural tradition rooted in respect for the natural world.